专注于SF6气体检测的专业化

Significance of controlling sulfur hexafluoride emission
Sulfur hexafluoride is one of the important compounds for environmental greenhouse gas emission reduction. The standard gas of sulfur hexafluoride was prepared by weight method. The preparation method, uniformity and stability of the standard gas were investigated. The experimental results show that the prepared sulfur hexafluoride standard gas has good reproducibility, good uniformity in the gas cylinder, and no instability trend during the 12-month development period. Compared with similar standard gases at home and abroad, the quantity value has a good consistency, and can meet the needs of environmental greenhouse gas monitoring.
Sulfur hexafluoride is one of the greenhouse gases stipulated in the Kyoto Protocol to be reduced. In 2011, The State Council issued the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" for the Control of greenhouse gas emissions, clarifying the control of sulfur hexafluoride greenhouse gas emissions, and requiring the strengthening of greenhouse gas measurement, emission factor calculation and data quality monitoring to ensure that the data is true and accurate. The Ministry of Environmental Protection proposed to carry out the pilot monitoring of urban greenhouse gases and greenhouse gases from pollution sources, and sulfur hexafluoride is an important monitoring index for environmental greenhouse gas monitoring. Sulfur hexafluoride in the atmosphere is mainly emitted by human activities, mainly from electrical equipment, magnesium and aluminum industry. Sulfur hexafluoride is non-toxic to humans, but a small amount of sulfur hexafluoride contributes more to the total radiation effect of greenhouse gases. Therefore, various departments need to strengthen the significance of controlling sulfur hexafluoride emissions.

SF6 gas has a century-old history, it is two French chemists Moissan and Lebeau synthetic artificial inert gas in 1900, around 1940, the United States military used it for the Manhattan Project (nuclear military). Commercially available in 1947. At present, SF6 gas is mainly used in the power industry. SF6 gas is used in 4 types of electrical equipment as insulation and/or arc extinguishing; SF6 circuit breakers and GIS (in this case, sulfur hexafluoride enclosed combination appliances, internationally known as "Gas Insulated Switchgear"), SF6 load switchgear, SF6 insulated transmission lines, SF6 transformers and SF6 insulated substations. 80% is used for high voltage power equipment.
It is obtained by the direct combination of fluorine and sulfur. The reaction also produces other fluorides of sulfur, such as sulfur decafluoride, which can be purified by disproportionating them with heat and then treating them with sodium hydroxide to remove the remaining sulfur tetrafluoride.
Original method: Burning sulfur in fluorine gas.
At present, the method of producing SF6 gas in chemical industry is mainly the direct combination reaction of elemental sulfur and excessive gaseous fluorine. That is S+3F2→SF6+Q (giving off heat). The composition and content of the impurities vary greatly due to the purity of the raw materials, the material of the production equipment, the process conditions and other factors, and the total content of impurities can reach 5%. It consists of sulfur fluorine compounds, such as: S2F2, SF2, SF4, S2F1O, etc. Sulfur fluoro compounds such as SOF2, SO2F2, SOF4, S2F10O, etc., and impurities brought into the raw materials such as HF, OF2, CF4, N2, O2, etc. If you want to use high-voltage electrical equipment, it is necessary to purify impurities in the crude product, and the synthesized SF6 gas also needs to go through a series of purification processes such as washing, alkali washing, pyrolysis (removal of highly toxic decafluorides), drying, adsorption, freezing, distillation and purification to obtain products with a purity of more than 99.8%. Then it is pressurized with a compressor and filled into a cylinder that is cooled to about -80 ° C and exists in liquid form.

 EN
EN




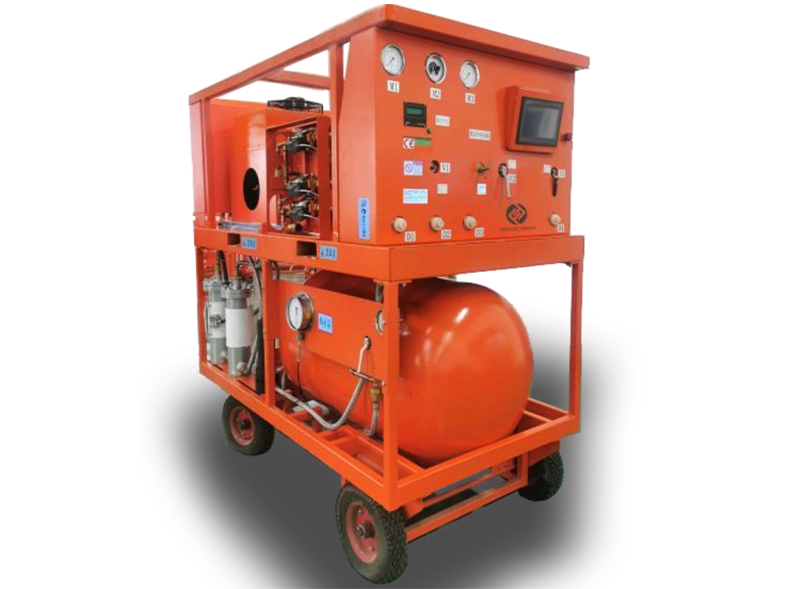
 上一条:
上一条: 
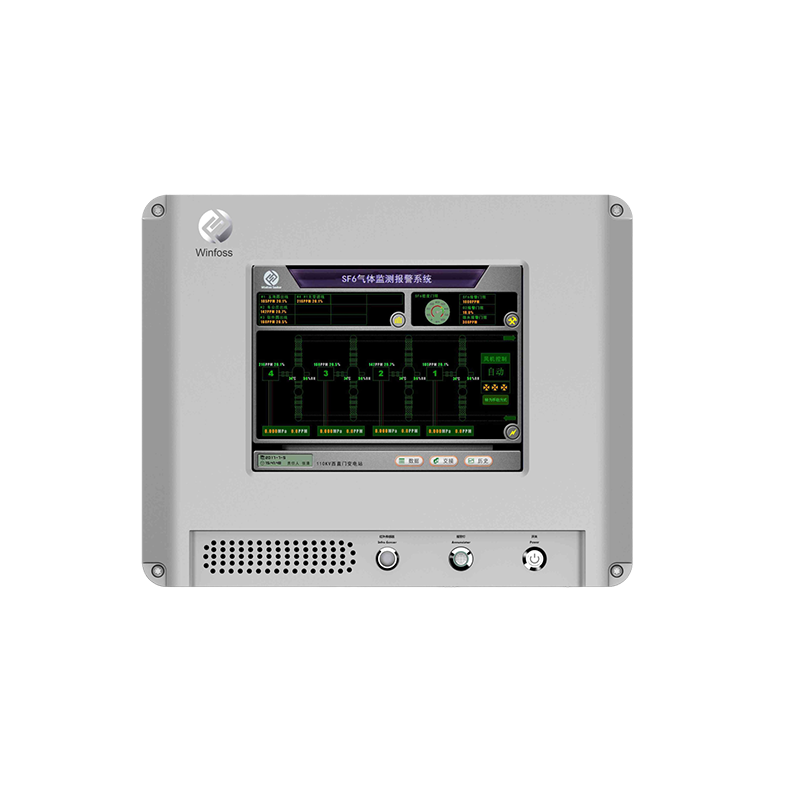








 沪公网安备31011802003762
沪公网安备31011802003762
