专注于SF6气体检测的专业化

What is the meaning of the critical temperature and critical pressure of SF6 gas?
From the basic physical characteristics of SF6 gas, it can be seen that it is relatively easy to liquefy gas compared with air. The state of SF6 gas depends on parameters such as its pressure and temperature.
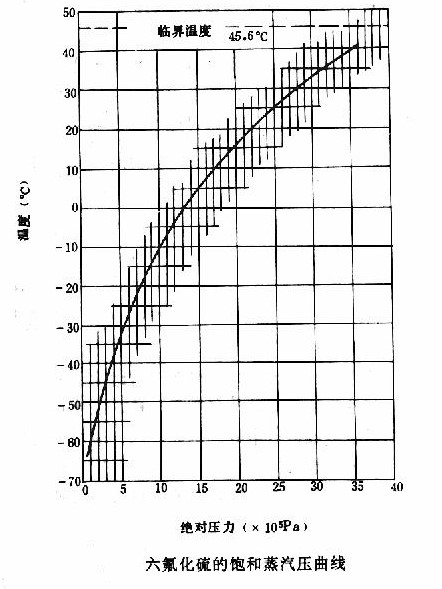
The critical temperature is the highest temperature at which a gas can be liquefied, and the lower the critical temperature, the less easily the gas can be liquefied. The critical temperature of SF6 gas is 45.6 ° C, indicating that the temperature is higher than 45.6 ° C in order to maintain a constant gaseous state. At this temperature, as long as the pressure is high enough, it can be liquefied, (for example, 0℃ is about 1.2Mpa to begin liquefaction), but for N2 there is no liquefaction problem at room temperature, and it can be liquefied only after the temperature is lower than -146.8℃.
Saturated steam pressure.
At the critical temperature, the density of the saturated vapor is the same as that of the liquid, the interface between them disappears, the gasification inversion is zero, and there is no difference in physical characteristics.

 EN
EN




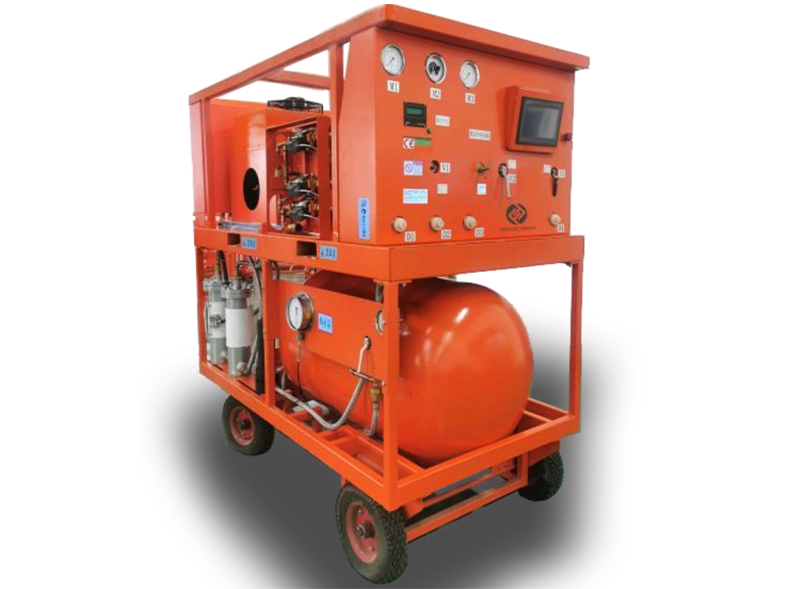
 上一条:
上一条: 
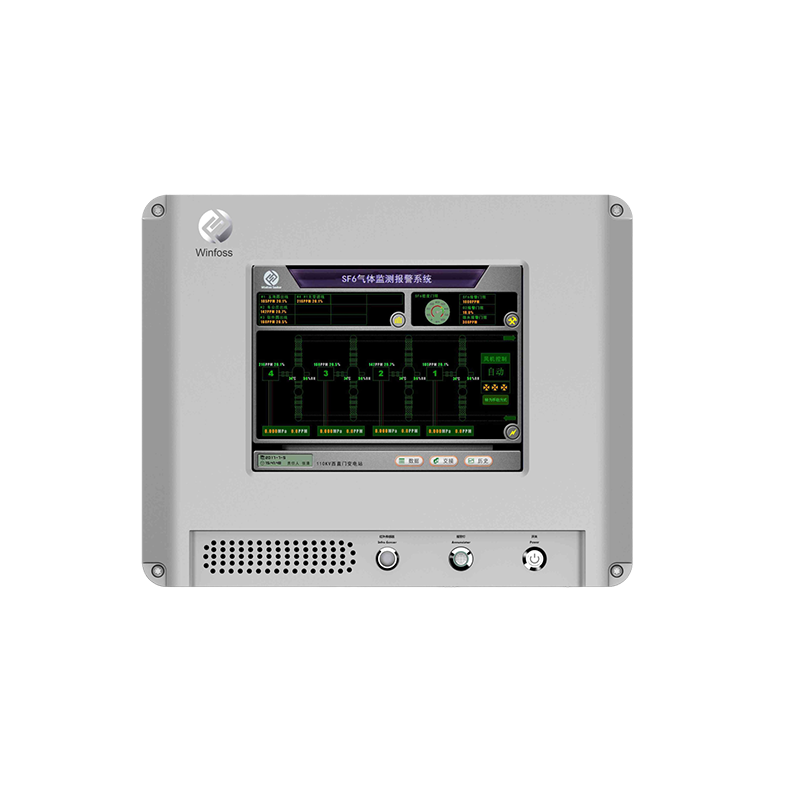
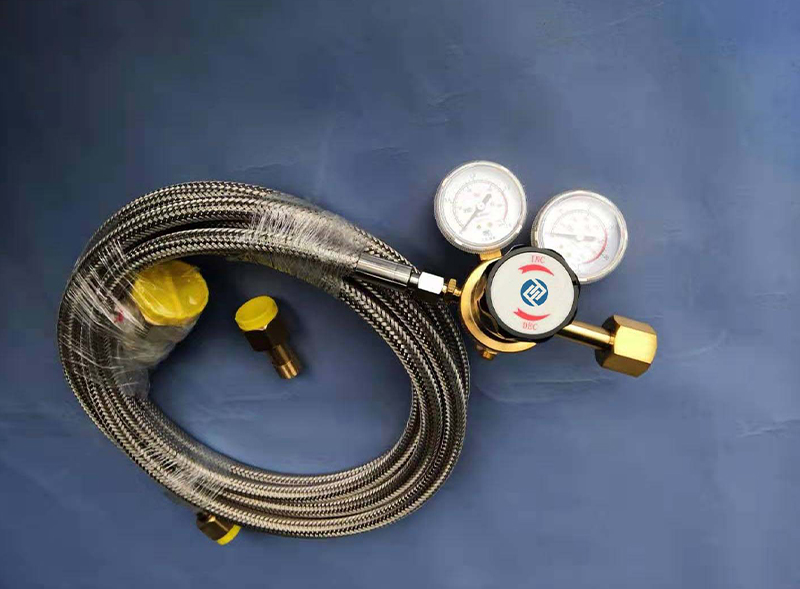








 沪公网安备31011802003762
沪公网安备31011802003762
