专注于SF6气体检测的专业化

What are the effects of SF6 gas on the human environment?
In the last hundred years, the earth's climate is undergoing a significant change with global warming as the main feature. This global warming is caused by both natural climate fluctuations and the greenhouse effect, which is enhanced by human activities. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change is the main goal of the United Nations Convention on Climate Change and the Kyoto Protocol, but China is facing more and more international pressure in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Hazard of sulfur hexafluoride to humans and animals
From a medical point of view, the degree of impact of various decomposition gases and products on the human body not only depends on the size of its toxicity, but also the size of the amount inhaled into the human body and the physical quality of each person. As an objective basis for judgment, Japan sets the allowable concentration of each animal substance to level 5. I.e. A - minimum lethal concentration; B - semi-lethal concentration (50% is fatal); C -- Short time residence limit, usually 15min; D - the lowest concentration at which toxic reactions occur; E -- for 8h a day, 40h a week of normal working time, most people work at this concentration, will not have adverse effects on health.
As early as 1979, Shanghai First Medical College and the Institute of Occupational Disease Prevention and Control of Shanghai Chemical Industry Bureau conducted a survey and animal tests on people who were engaged in or exposed to sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas for a long time.
In the occupational epidemiological survey of the workers of the two enterprises that produced and used sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas, the workers who were similar in age, sex, labor intensity, professional service, smoking or not were grouped and compared, and no obvious harm was found to the health of the workers. However, from the point of view of the statistical incidence of symptoms, the number of people showing weakness, poor memory, sore throat, chest tightness is more.
Animals (female rats and mice) were exposed to different concentrations of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) as a new gas or (exposed to an electric arc) in a gas grouping chamber for group acute and subacute static exposure tests. As a result, the acute static exposure test showed no abnormalities, while the subacute static exposure test showed mild submicroscopic structural changes in the pulmonary capillaries of one rat under electron microscopy. Whether it is caused by sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas is difficult to determine due to the limited number of animals tested.
The greenhouse effect means that gases such as carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can heat up the Earth's surface through short-wave radiation from the sun. At the same time, it blocks the Earth's surface from emitting long-wave radiation into space, thus warming the atmosphere. Because this role of carbon dioxide and other gases is similar to the role of "greenhouse", it is called "greenhouse effect", and carbon dioxide and other gases are called "greenhouse gases". At present, it is found that there are six kinds of greenhouse gases emitted by human activities, they are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, among which three kinds of fluoride. Among them, CO2 has the greatest impact on the greenhouse effect, accounting for 60%, while the impact of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas only accounts for 0.1%, but sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas molecules have potential harm to the greenhouse effect, because the impact of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas molecules on the greenhouse effect is 25,000 times that of CO2 molecules. The sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas emitted into the atmosphere has a very long life of about 3400 years. Today, about 21 billion CO2 gases are released into the atmosphere each year, and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas is equivalent to 125 million tons of CO2 gas each year.

 EN
EN




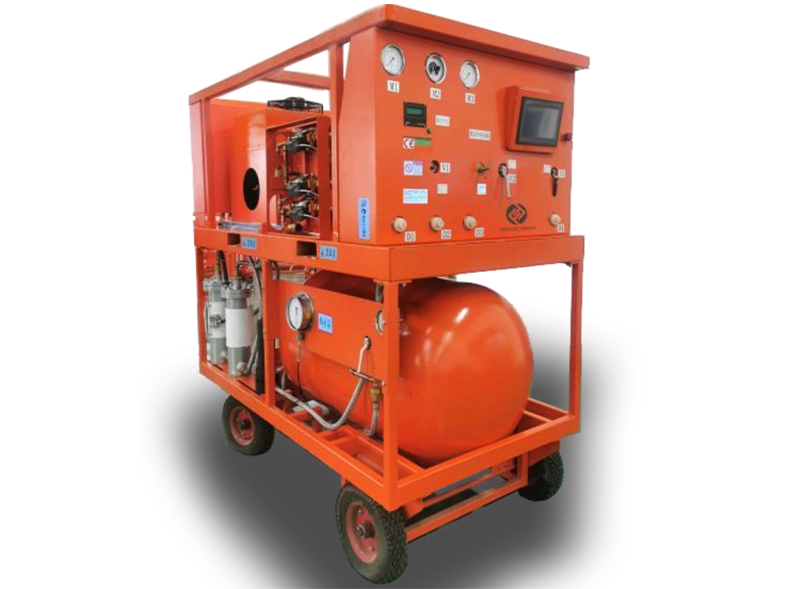
 上一条:
上一条: 
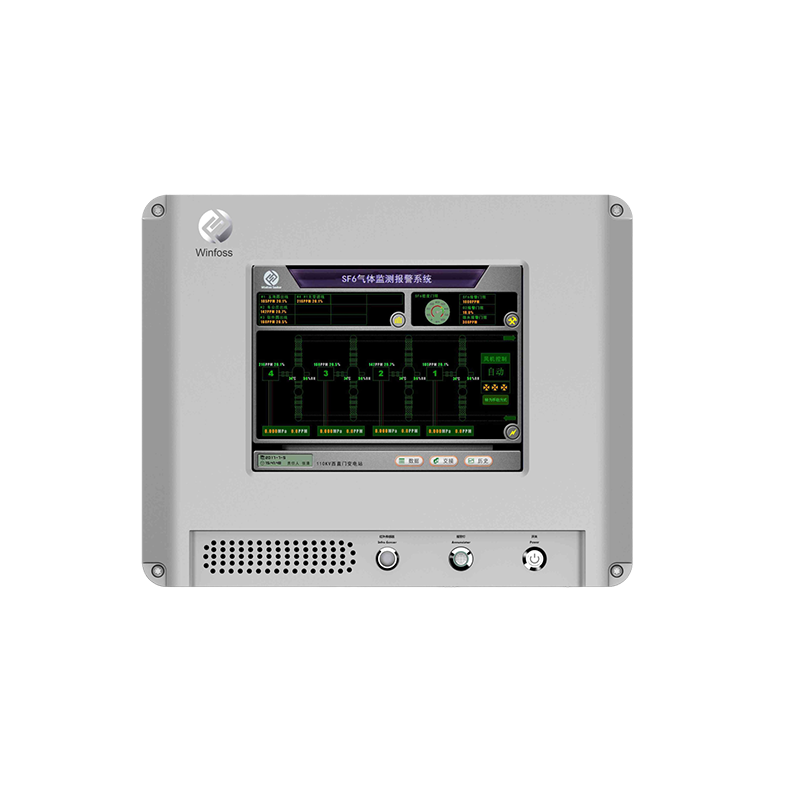
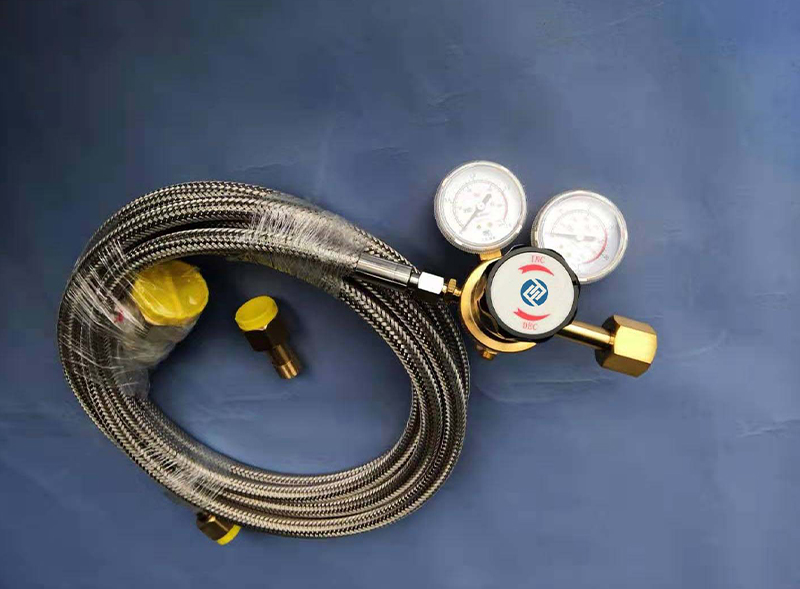








 沪公网安备31011802003762
沪公网安备31011802003762
