专注于SF6气体检测的专业化

SF6 gas applications in the energy industry
SF6 gas applications in the energy industry
As an excellent insulating and extinguishing medium (its extinguishing performance is 100 times faster than air), SF6 gas has been used in medium and high voltage circuit breakers for decades, proving to be by far the most suitable insulating medium for use in medium and high voltage circuit breakers.
The application of SF6 gas makes the circuit breaker design more compact, more material saving, and at the same time has higher breaking capacity and equipment safety.
SF6 gas applications in other industrial fields
In addition, SF6 gas is also used in other industries, such as in the semiconductor manufacturing industry, display and micro-technology industries, primarily as an etching gas for the production of hyperfine structures (aka wafers).
In medical technology, SF6 gas can be used in ultrasound detection and ophthalmology. SF6 gas is also used in X-ray inspection equipment, radar systems, and particle accelerators.
Recovery and reuse of SF6 gas
Although SF6 gas is an excellent insulating and arc-extinguishing medium, it is still necessary to understand other properties of SF6 gas:
SF6 gas is a fluorinated gas that has a high global greenhouse effect and is one of the six gases that must be monitored under the Kyoto Protocol
The global greenhouse effect of 1 kg of SF6 gas is 25,000 times that of 1 kg of CO2 gas, and the lifetime of SF6 gas in the atmospheric environment is 3,400 years.
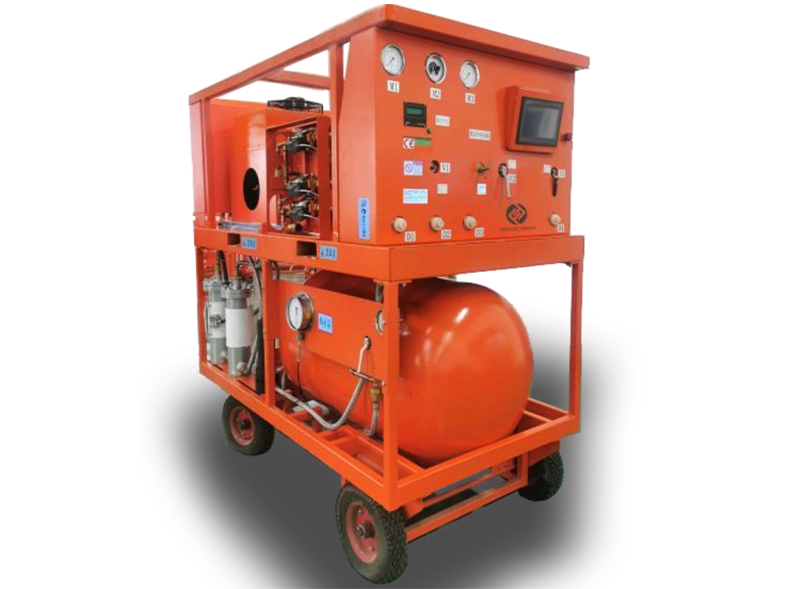
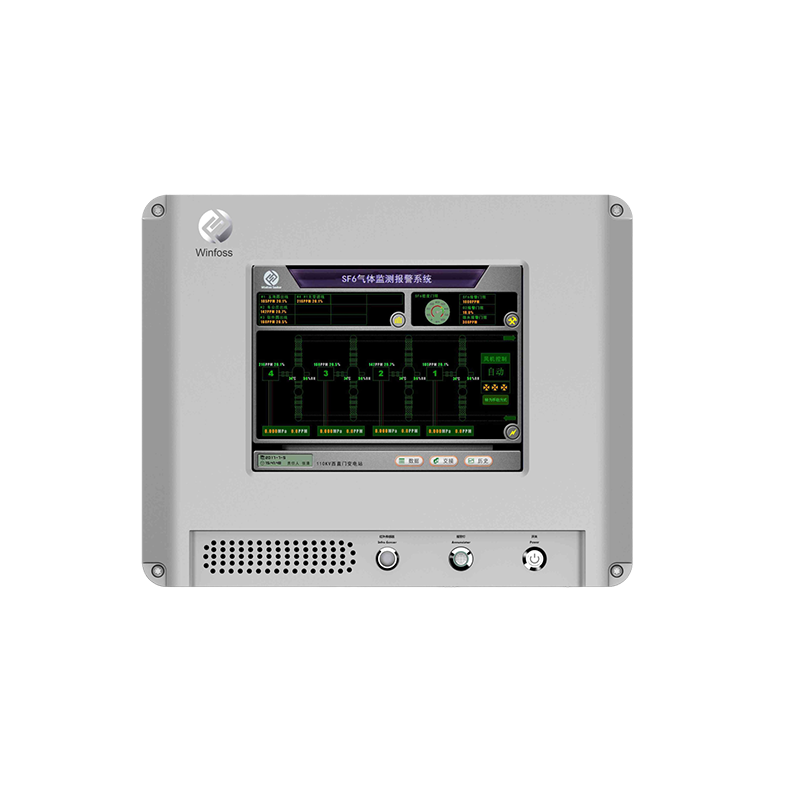
Therefore, SF6 gas must be used in a closed-loop system to avoid emissions to the atmosphere. As a manufacturer of zero-emission SF6 gas treatment equipment, this is also the core competence of WINFOSS.
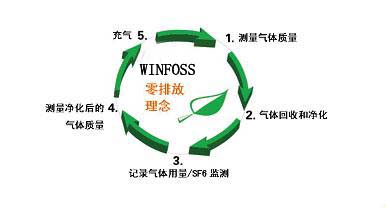
Based on “ Zero emissions ” And “ Highest gas reutilization” We pursue three core propositions:
Environmental protection
Low operating cost
Comply with relevant legal requirements
To this end, we propose “ Zero emission concept “ A closed technical loop is designed for all SF6 gas treatment processes to achieve high reliability and zero emissions.
In order to realize the above concept, it is necessary to have technologically advanced and efficient equipment and devices.
The SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride) gas transformer is undergoing airtight tests
Characteristics and arc-extinguishing principle of sulfur hexafluoride gas
1. Basic characteristics of sulfur hexafluoride gas
SF6 is currently the best arc extinguishing and insulating medium used in high voltage electrical appliances. It is colorless, tasteless, non-toxic, will not burn, chemical properties are stable, and will not produce chemical reactions with other materials at room temperature.
SF6 is formed by combining fluorine, the most reactive of the halogens, with sulfur. The molecular structure is a completely symmetrical octahedron, sulfur atoms in the center, six corners are fluorine atoms, fluorine and sulfur atoms are covalent bonds, SF6 molecular weight is 146, about 5.1 times the molecular weight of air, so the same volume of SF6 gas is much heavier than air. So far, the manufacturing method commonly used in industry is the direct combination of elemental sulfur and excess gaseous fluorine.
(1) State parameters of sulfur hexafluoride gas
Stationary gas can use three parameters to explain the state of the gas, called the three state parameters, namely pressure P, density γ And the temperature T. • There is a simple relation between the state parameters of ideal gas, that is, the equation of state of gas P= γ RT • The molecular mass of SF6 gas is large, and the interaction between molecules is significant. When the gas pressure is higher than 0.3MPa, the intermolecular attraction is strengthened with the increase of gas density and the decrease of intermolecular distance, and the gas pressure change characteristic no longer conforms to the equation of state of the ideal gas. To accurately calculate the relationship between SF6 gas state parameters, a more practical method can be used. The Bridgman formula.
The critical temperature of SF6 gas is high. The critical temperature represents the highest temperature at which the gas can be liquefied, and the critical pressure represents the pressure required to liquefy the gas at the critical temperature. The critical temperature of SF6 gas is as high as 45.6°. C, indicating that SF6 gas will liquefy at constant temperature as long as the pressure is high enough. The ability of SF6 gas to liquefy depends on its saturated vapor pressure. When the pressure of a gas is higher than its saturated steam pressure, the gas liquefies.
The thermal conductivity of SF6 is not as good as that of air, its thermal conductivity is lower than that of air, and 30% lower than that of air at constant temperature. However, due to its low viscosity and high density, and large molecular weight, the heat capacity is large, and taking into account the convection effect, the total heat transport characteristics are 2-5 times better than air.

 EN
EN




 上一条:
上一条: 








 沪公网安备31011802003762
沪公网安备31011802003762
