专注于SF6气体检测的专业化

What is the difference and function between pressure gauge and density relay used in SF6 circuit breaker?
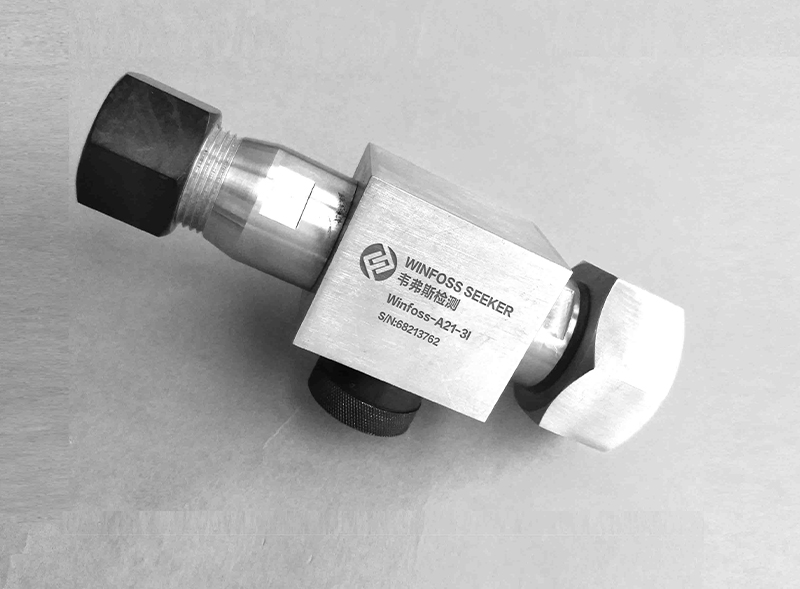
Pressure gauge is a monitoring function, that is, the detection of system pressure, density relay is on the one hand is to monitor the change of system pressure, on the other hand is to control and protect the function, density relay can be set in different pressure states of the open and close signal contact. There are usually alarm contacts and latching contacts, and the pressure gauge is without contacts, which is the difference between the two. Density relays, pressure relays with temperature compensation, are mainly used to send alarm signals and lock signals.
A gas pressure gauge installed on the break to monitor the pressure change of SF6 gas in the electrical equipment. The density meter monitors the leakage of gas in the electrical equipment, and the main role of the density relay is to monitor the SF6 gas density in the circuit breaker, which is said to be the density, in fact, the pressure monitoring with temperature compensation.
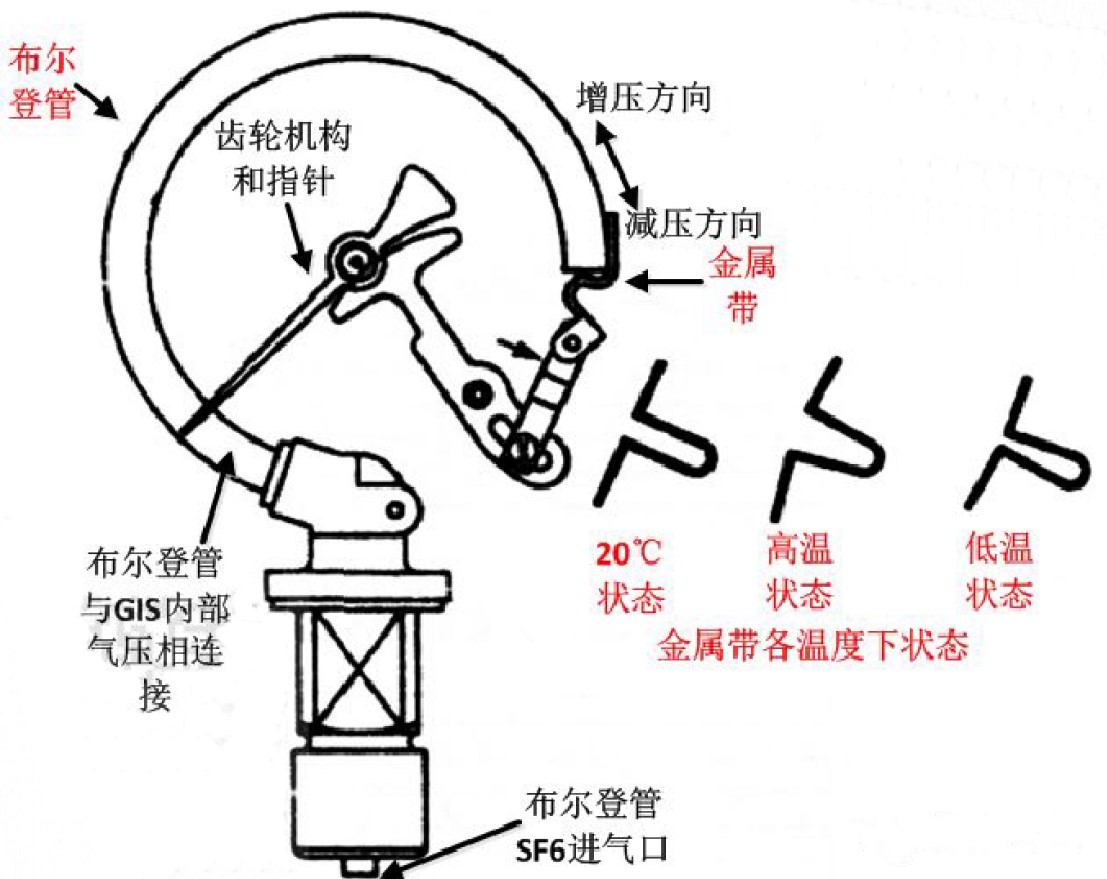
SF6 gas density: In a closed container, the SF6 gas pressure at a certain temperature can represent the density of SF6 gas. It is customary to take the SF6 gas pressure at 20℃ as the standard value. In the field verification, under different ambient temperatures, the measured pressure value should be converted to its corresponding pressure value at 20℃ to judge the performance of SF6 density relay. Density relays play a controlling and protective role in monitoring electrical equipment. Generally, the domestic installation density meter monitors the open circuit or GIS leakage, and some pressure and gas density relays are combined to detect the leakage of equipment.
SF6 density detection is the use of Bourdon tube pressure measurement, Bourdon spring or Bourdon tube is a hollow coil spring, gas from the inlet into the Bourdon spring, forcing the spring to extend, drive the pendulum rod to move left, push the gear rod counterclockwise rotation, the needle deflecting clockwise, indicating the pressure reading. If the pressure rises, the Bourdon spring extends further so that the needle continues to deflector clockwise. If the pressure is reduced, the Bourdon spring contracts, moving the pendulum bar to the right, rotating the gear bar clockwise and deflecting the pointer counterclockwise.
In the absence of leakage in equipment filled with SF6 gas, a change in temperature will cause a change in pressure. If the ambient temperature decreases, the pressure will decrease; conversely, if the ambient temperature increases, the pressure will increase. In the absence of temperature compensation, if the equipment leaks air, but the ambient temperature is high, the meter still indicates the specified pressure, if the equipment does not leak air, but the ambient temperature is low, the meter will indicate lower than the specified pressure. In this way, it is not possible to correctly determine whether the equipment is leaking. In order to detect whether the equipment is leaking, it is necessary to use compensation devices to eliminate the influence of temperature changes on the pressure indication.
SF6 density relays generally provide two or more pairs of contacts to monitor the gas pressure value in the SF6 equipment, when the pressure drops to its alarm value, the density relay will send an alarm signal, indicating that the equipment needs to recharge the air, for the circuit breaker, when the pressure drops to the locking value, the circuit breaker can not be closed.
The SF6 gas in the circuit breaker needs to maintain a certain density to ensure its insulation performance and arc extinguishing performance, so it is a locking contact. At this time, if the locking pressure is lower than that, the circuit breaker should be locked so that it cannot operate, otherwise it will cause an accident.

 EN
EN




 上一条:
上一条: 








 沪公网安备31011802003762
沪公网安备31011802003762
