专注于SF6气体检测的专业化

What are the principles of SF6 gas leak detection?
There are many ways to detect SF6 gas leaks. Because sulfur hexafluoride is a negative electric gas, it has the characteristic of absorbing free electrons to form negative ions, and the methods of leak detection are mostly made use of this characteristic. There are four commonly used sulfur hexafluoride gas leakage detection methods: ultraviolet ionization detection, electron capture detection, vacuum high frequency ionization detection and negative corona discharge detection.
1, ultraviolet ionization detection principle: ultraviolet ionization detection is the use of ultraviolet light to detect the oxygen and sulfur hexafluoride gas ionization, according to their ion migration speed and electron absorption capacity differences, quickly and easily determine the concentration of trace sulfur hexafluoride contained in the detected gas. The detection principle is that the ultraviolet lamp in the ultraviolet detector pulsates at a oscillation frequency of 2KHZ, emitting 1849×10-10m ultraviolet light. Ultraviolet light is directly irradiated on the photoelectric surface through the network of accelerating electrodes, so that the photoelectric surface emits free photoelectrons. Oxygen and sulfur hexafluoride in the measured gas are adsorbed on these photoelectrons by passing the measured gas between the photoelectric surface and the accelerating electrode. These photoelectrons are ionized into an ionic state under the action of a voltage applied between the photoplane and the accelerator pole, and move towards the photoplane at their respective migration speeds. Because the electronegativity of oxygen and sulfur hexafluoride gas is not the same, the photoelectron capture ability is not the same, the formation of different migration speed, using the phase difference of the ion flow formed by this speed difference, the phase change of the ion flow can be detected, the existence and concentration of sulfur hexafluoride gas can be checked.
2, electron capture detection principle: electron capture detection uses radioactive isotope Ni63 as the detector ion emitter. This type of instrument only produces signals for gases that are electronegative (such as halogen substances and substances containing O, S, and N molecules), and the sensitivity increases with the increase in the electronegativity of the substance. The detection principle is that when the carrier gas passes through the radioactive source, the high capacity electrons of the beta ray ionize the carrier gas to form positive ions and slow electrons, and then migrate to the positive opposite electrode to form a base flow. When the negative electric gas (such as sulfur hexafluoride) enters the detector from the probe, it captures the slow electrons in the detector to generate negative ions, and the negative ions in the electric field are lower than the free electrons, and the negative ions of the gas to be tested are combined with the positive ions of the carrier gas to become neutral chemicals, which are taken out of the detection room by the carrier gas, and the original base flow is reduced. The reduction of the base flow is proportional to the concentration of the measured gas. In this way, the changed base flow is output as the concentration indication signal through the signal amplifier, so as to meet the requirements of detecting the concentration of the gas.
3, negative corona discharge detection principle: negative corona discharge detection is based on the principle of high-frequency pulse negative corona continuous discharge effect, according to the negative electronegative effect of sulfur hexafluoride to detect the leakage gas. The detection principle is to use the air pump is the gas through the purification layer (remove water and dust) into the detector, the detector under the action of pulsed high pressure corona continuous discharge effect, when the gas with negative gases (such as sulfur hexafluoride, halogens, fluorohalocarbons, etc.), these negative gases in the detector corona electric field plays a role in the suppression. The stronger the electronegativity in the gas, the higher the concentration of the substance, the more suppressed the corona effect, the corona discharge current will be reduced, these with the concentration of the negative gas and change the corona current through the signal amplification into the concentration indicator value, at the same time, the alarm circuit has been set according to the size of the current signal and issued a concentration limit warning signal. The detector of this kind of instrument is easy to be polluted by dust, oil smoke and corrosive gases in the air, and the sensitivity and performance of the instrument are reduced, so the instrument should be cleaned regularly, usually with anhydrous ethanol injected into the detector repeatedly washed several times, and can be re-calibrated after drying.
4, the principle of high frequency ionization measurement method: the air contains different concentrations of sulfur hexafluoride gas or various halogen gases under the action of high frequency electromagnetic field ionization degree is different. The detection principle is as follows: The instrument consists of a probe and a pump body. The high-frequency electric field electrode on both sides of the instrument's gas ionization chamber and the high-frequency oscillation coil form the resonant circuit and energy output circuit of the high-frequency oscillator. The needle valve of the probe can adjust the intake volume to match the pumping rate of the pump so as to maintain a certain vacuum degree in the gas ionization chamber, so that the measured gas is under the action of a low energy high-frequency electromagnetic field. It has sufficient ionization. The high frequency electric and magnetic fields produced by the high frequency coil act on the rarefied gas in the ionization chamber, resulting in high frequency electrodeless ionization. When the air passing through the ionization chamber does not contain sulfur hexafluoride or halogen gas, the cavity absorbs the energy given by the high-frequency electric and magnetic fields, resulting in a significant decrease in the Q value in the resonant loop, and at the same time, the oscillation amplitude of the high-frequency oscillator is greatly reduced. However, when the air contains negative gases such as sulfur hexafluoride or halogen gas, because sulfur hexafluoride and halogen gas are electron trapping gases, A large number of free electrons can be captured in the ionization chamber, so that the ionization degree in the ionization chamber is weakened, the oscillation amplitude of the oscillator is increased, and the rising amplitude is proportional to the negative electric gas concentration of the measured gas, so that the signal is converted into a concentration indication through the signal amplifier.

 EN
EN




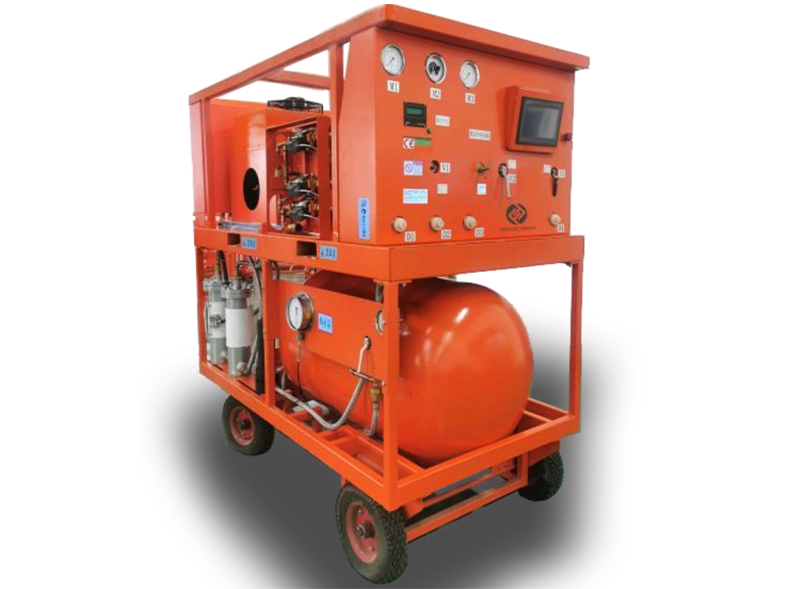
 上一条:
上一条: 
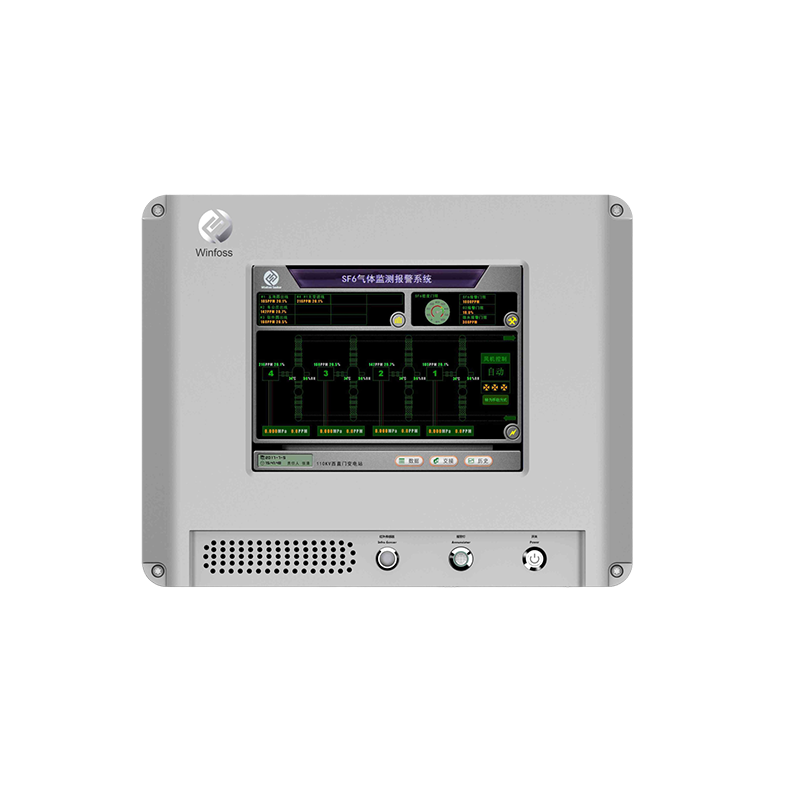








 沪公网安备31011802003762
沪公网安备31011802003762
