专注于SF6气体检测的专业化

At present, what are the commonly used SF6 gas humidity detection methods and detection instruments in power systems?
According to the application of SF6 gas electrical equipment in the power system, it has the characteristics of low humidity. At present, the commonly used SF6 gas humidity detection methods mainly include gravimetric method, electrolytic method, resistance and capacitance method, and dew point method.
The field commonly used testing instruments mainly include electrolytic type, resistance-capacitance type and dew-point type.
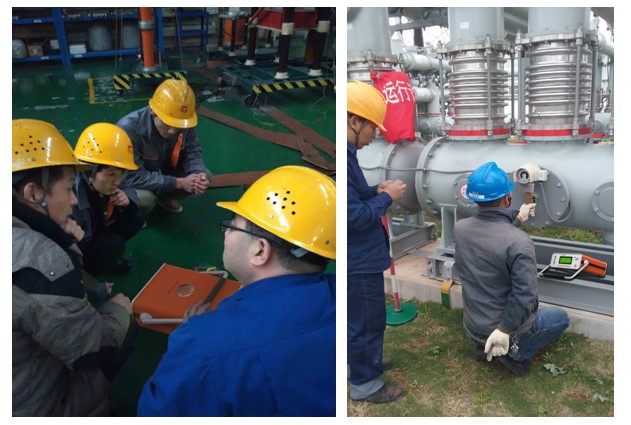


The circuit breaker has strict requirements on the purity and water content of SF6. In the case of internal flashover, a variety of SF6 decomposition products will be generated, and atmospheric moisture will also penetrate into the gas insulation equipment during normal operation. Under high air pressure, excessive moisture has a serious impact on the surface flashover voltage of solid insulation parts in gas insulation equipment, and even leads to internal flashover accidents. Some active impurities, such as HF, SO2, etc., will have a corrosive effect on various components in gas insulation equipment. Some scale decomposition products are also toxic, once leaked out will pollute the environment, affecting the health of workers. Excessive moisture will reduce the insulation strength of gas insulated equipment. Therefore, first of all, we should ensure that the SF6 gas filled into the electrical equipment is qualified, and prevent water from entering the gas chamber during the inflation operation.
The relevant regulations of our country stipulate that the water content of the new SF6 gas used in circuit breakers must be ≤8×10-6. The water content of SF6 gas in the circuit breaker in operation, and the water content of the measured gas after the mechanical characteristics test should not exceed 150×10-6.
1. Quality Law
In this method, the measured volume of SF6 gas is passed into the weighing test tube of heavy magnesium acid (or phosphorus pentoxide) as a desiccant, and the moisture content of the gas is obtained from the increase of the mass of the test tube. This method is often referred to as the arbitration method and is used to verify and calibrate the original accuracy of other moisture measuring instruments. The control of the test environment, the measurement of the gas volume, and the weighing of the absorption system are all very important. The schematic diagram of the device for measuring the water content of SF6 gas by mass method is shown in Figure 7-5.
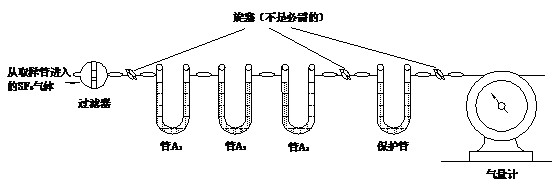
Device for measuring water content in SF6 gas by mass method
2. Electrolysis
Electrolysis uses a pair of electrodes (platinum or rhodium) coated with phosphoric acid to form an electrolytic cell and apply a constant DC voltage between the poles. The moisture of the measured gas is absorbed by the hygroscopic agent (P2O5), and electrolytically reduced under the action of electric current, releasing oxygen and hydrogen. When the absorption and electrolysis reach a balance, the water content of the gas can be obtained by using the relationship between the electrolytic current and the water content. This method is a common and practical method, the measuring instrument can directly read the mass fraction of micro-water content, simple and stable operation, suitable for continuous online analysis. The electrolysis method has few interference factors, high data repetition rate, high accuracy and simple operation when measuring the water content of SF6 gas, especially when measuring the low water content. However, the shortcoming of the electrolysis method is that the electrolytic efficiency of the electrolytic cell decreases with the increase of the use time. Under normal circumstances, the electrolytic efficiency is less than 85%, and the electrolytic cell should be stopped.
3, dew point method (cold mirror method)
The method is to measure the condensation and humidity of the moisture contained in the gas. The measured gas passes through a metal mirror in a sealed pool, and the mirror humidity is monitored manually or with the help of a photocell to maintain a stable amount of moisture condensation. When the temperature of the test system is slightly lower than the saturation temperature of water vapor in the test gas (dew point), the water vapor condensation. The mirror temperature measured by thermocouple is the dew point. The moisture content in gas can be obtained from the conversion formula or comparison table of dew point and gas moisture content. The instrument used in the dew-point method is more complicated and requires liquid nitrogen as refrigerant, which has high cost and large volume. The measurement accuracy is closely related to the quality of the instrument itself, which is not convenient for field use.

 EN
EN




 上一条:
上一条: 








 沪公网安备31011802003762
沪公网安备31011802003762
