专注于SF6气体检测的专业化

SF6 high voltage electrical equipment SF6 leakage amount and leakage rate calculation test content and method
Purpose and scope of application
The purpose of this operation instruction is to test whether the performance of the circuit breaker SF6 gas quantitative leak detector meets the standard requirements
2. Reference standards
"Electric Power Equipment handover and preventive experimental Procedures" State Grid Company DL/T596 GB 50150-2006
DL/T 846.6-2004 "High voltage test equipment general technical conditions Part 6: sulfur hexafluoride gas leak detector"
JJG 914-1996 "Sulfur hexafluoride leak detector Verification Regulations"
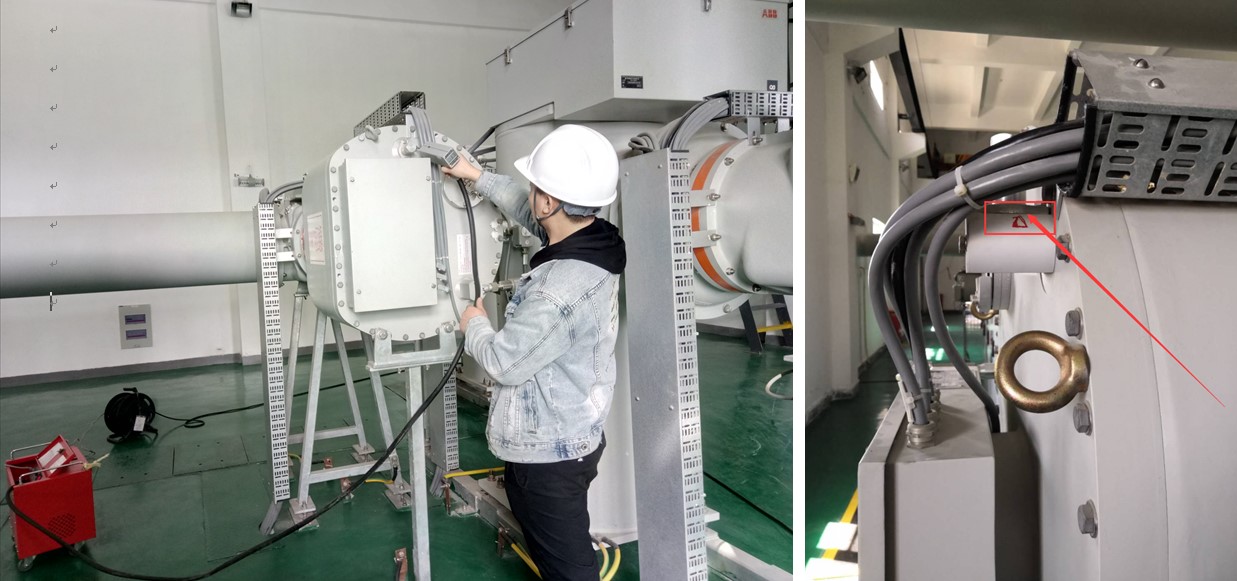

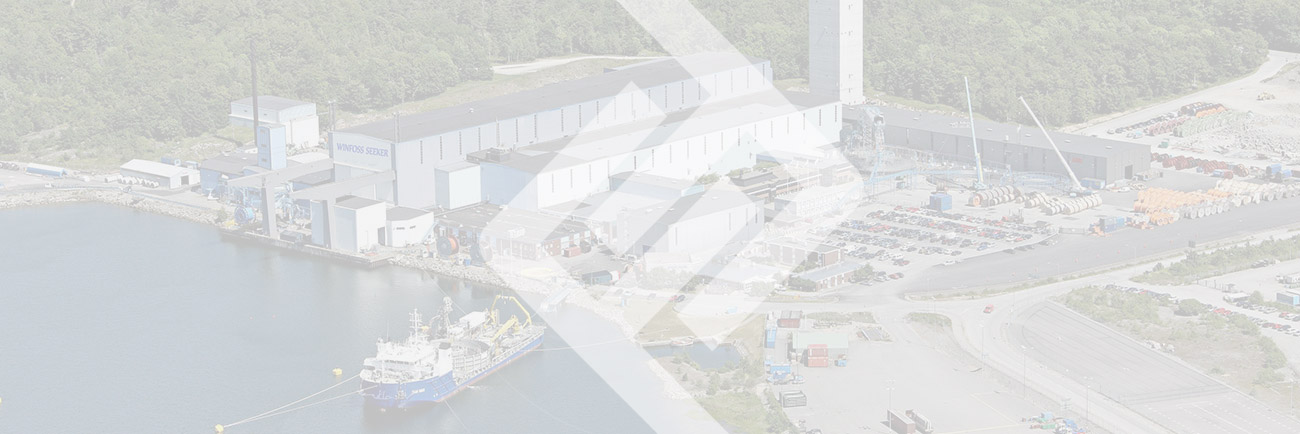
Third, the content and method of calculation test for SF6 leakage and leakage rate
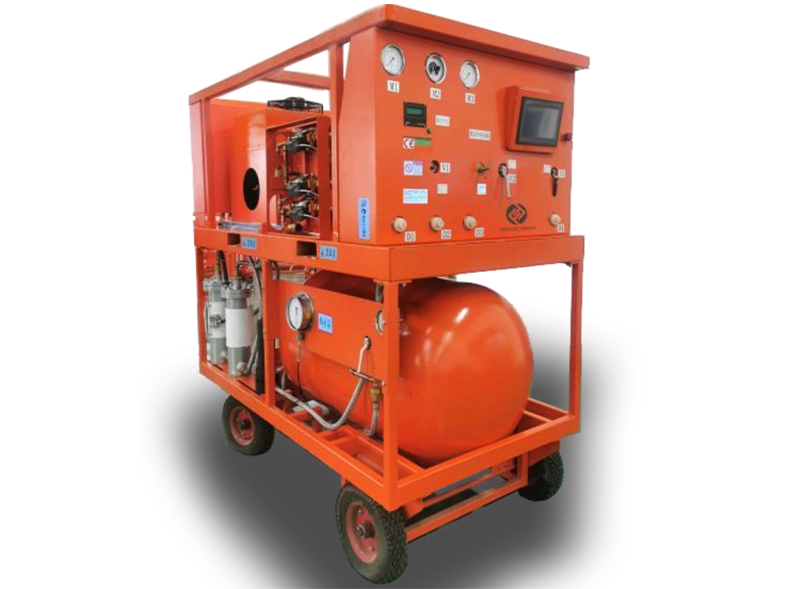
The sealing test is to determine whether the annual leakage rate of the gas chamber is qualified by detecting the leakage amount of SF6 gas. The control standard is that the annual leakage rate of each independent gas chamber is not more than 0.5%; For the calculation of SF6 leakage and leakage rate, generally using the dressing method (buckle method), which is a fine work, the leak detection tool used must be a quantitative leak detector, the accuracy must be higher than 1ppm, and it must be a stable detection tool.
The implementation procedure is: vacuum inspection →SF6 gas → leak inspection. The specific process is: After the GIS is tested by vacuum and the SF6 gas is stationary for 5h, the flange interface is wrapped with a plastic film, and the test is carried out after 24h.
Result determination
The local dressing method is used, and after 24h detection, if there is a concentration of SF6 gas in the film greater than 30ppm, the gas leakage rate of the gas chamber is unqualified. If the concentration of SF6 gas in all wrapped films is less than 30ppm, the gas leakage rate of the chamber is considered acceptable.
Calculation of air leakage:
G=(k/Δt)*v*ρ*t (克) (1)
Where :k= measured concentration value (volume ratio);
V= test volume (liters), equal to the volume of the cover minus the volume of the part under test, that is, v=v cover -v object under test
It should be noted that the v test object, when partially bandaged, the test object is only a part of the volume that is bandaged.
t= the working time of the tested object (hours), if the air leakage in a year, t=365*24=8760 hours
Δt= interval of measurement, if the test is performed 24 hours after bandaging, then Δt=24 hours
Calculation of air leakage rate
M=(g/Q)*100/%
Where Q= the total weight (grams) of SF6 gas filled into the equipment or container
Example: Measure the leakage rate of a group of 110 kV SF6 combined electrical outlet circuit
Known: cover volume V cover =29.0m3 Outlet loop volume V measured object =6.5m3, SF6 gas filled 120Kg
Δt=3.5 hours, ρ=sf6 density (6.14 g/L) measured concentration k=2*10-5
Find the annual leakage rate M
Solution :V= V cover =29.0m3-6.5m3=22.5m3= 22,500 liters, substitute (1)
g=(2*10-5*22500*6.14*24*365)/3.5= 6915g
From formula (2) :
M = 6915 / (120 * 1000) * 100% = 5.76%
The implementation procedure is: vacuum inspection →SF6 gas → leak inspection. The specific process is as follows: after the GIS is vacuum detected and the SF6 gas is stationary for 5h, the flange interface is wrapped with a plastic film, and the test is carried out after 24h. If the concentration of SF6 gas in a film is greater than 30ppm, the gas leakage rate of the air chamber is unqualified. If the concentration of SF6 gas in all wrapped films is less than 30ppm, the gas leakage rate of the chamber is considered acceptable.
It is recommended that enterprises adopt enterprise standards higher than this standard, and the contact method detection is not less than 1PPM. The bandaging method is not higher than 10PPM.

 EN
EN




 上一条:
上一条: 








 沪公网安备31011802003762
沪公网安备31011802003762
